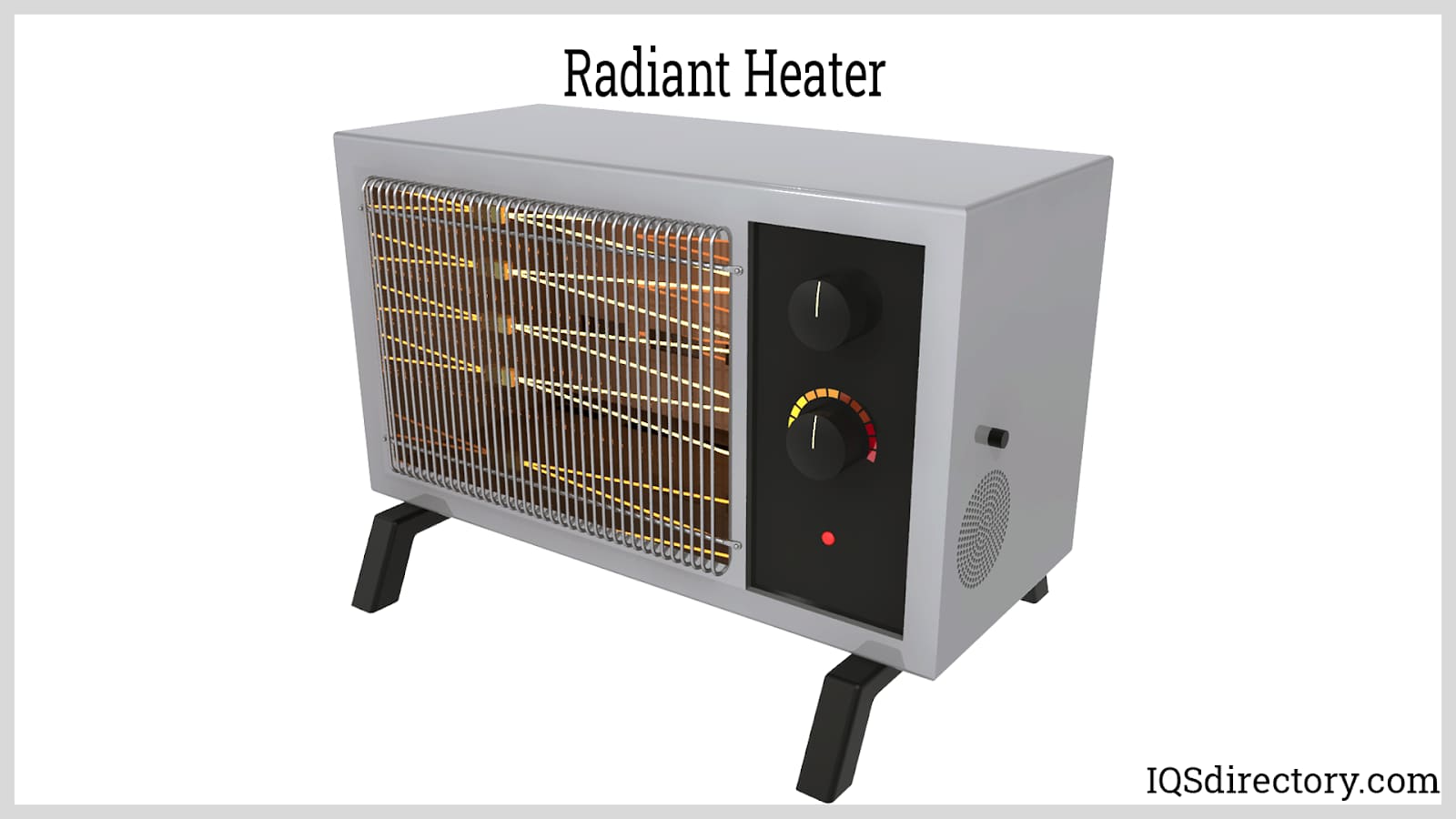
Infrared heaters, also known as radiant heaters, are heaters that emit infrared heat waves. Infrared heat waves are defined as long electromagnetic waves that are located near the visible light section of the electromagnetic spectrum. As this definition implies, infrared heaters emit infrared light energy that we cannot actually see. Rather, we can only feel it. For this reason, people often compare infrared heaters to the sun. Read More…
Economical, highly efficient, and satisfyingly effective Solaira™ quartz electric infrared heaters offer residential and commercial solutions that are second to none. We utilize the most up-to-date PHILIPS tm HeLeN quartz infrared technology to provide instant and directional radiant heat that is equivalent to the comfort of the sun actually warming you up and not just the air around you.
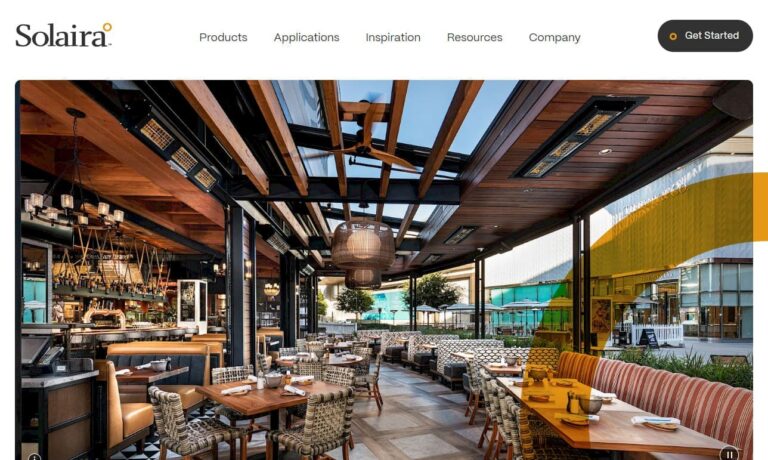
Area controlled heat that is clean and fast describes our infrared heaters. We have infrared heaters for everyone’s needs to choose from. Choose from portable heaters, infrared forging heaters, outdoor heaters, radiant heaters, electric infrared heaters and more. Our heaters are seen everywhere!
Mor Electric Heating offers Salamander electric ceramic infrared heating elements and panels, comfort spot heaters, pet and animal comfort heaters, portable comfort space heaters and industrial processing heaters. We can also custom design radiant heating panels for your needs.
Easy Radiant Works provides leading energy efficient infrared heating solutions. We offers a complete range of gas fired low and high intensity infrared heaters for industrial, commercial, sports facilities, hospitality, agricultural and residential applications throughout the United States. Our innovations continue to evolve; superior technology & performance remain constant. Contact us today to ...

More Infrared Heater Manufacturers
Also, like the sun, infrared heaters warm up only the areas to which they are exposed or have direct contact. Think of it this way: when you are under tree shade, the infrared light energy of the sun is blocked and you stay cool, but as you come out in the light, you feel the warmth. Industrial infrared heaters work on the same principle.
Infrared Heater Applications
Infrared waves give off a large amount of radiant heat, which can be easily absorbed by a variety of different surfaces. The infrared waves are produced by a heating element, and the heat it generates does not need to rely on transportation by air molecules or any other medium. For these reasons, infrared heaters have a wide variety of applications.
Using infrared heaters, you can heat spaces as large as a warehouse or as small as a bedroom. Some of the applications for which customers typically purchase infrared heaters include small space heating, room heating, central heating, process heating, industrial oven heating, plastic welding, glass processing, and drying of coatings. People can also use infrared heating for relief from arthritis-induced joint pain and for animal care in veterinary clinics and zoos.
History of Infrared Heaters
In 1800, a German-British astronomer named Sir William Herschel discovered infrared radiation. He made this discovery while he was experimenting with a spectrometer, an instrument he had built himself in order to measure the magnitude of radiant energy at various wavelengths. It consisted of a prism that caught and dispersed sunlight, a cardboard panel with a slit for one color at a time to pass through, and three mercury thermometers encased in glass. With it, he discovered that, on the light spectrum, red light experiences the highest degree of temperature change.
Hershel’s discovery was very important, but no one really made use it for over 100 years. It became popular during World War II. It was at this time that manufacturers found they could use infrared heat in heat lamps to quickly dry and cure lacquers and paints that they applied to military vehicles and supplies. Once the war ended, manufacturers shifted their use of infrared heat drying and cooling to the automotive industry. During the mid 1950s, they streamlined the process by creating infrared tunnels through which they could direct cars during production.
Today, infrared heating is one of many heating, drying, and curing methods we have in this world. However, infrared heaters continue to be popular due to their cost-effectiveness, versatility, and energy efficiency.
Infrared Heater Design
Manufacturers construct infrared heaters from a heating element and a reflective surface, which is used to direct heat waves a certain way. In order to prevent burning or injury, they also encase the heating element in a protective enclosure.
Heating Element Materials
There are some infrared heaters that make use of metal, ceramic, or glass as a heating element, but most often, they are made using a quartz heating element. This is because quartz is able to heat more quickly than any other heating element. Another heating element is tungsten, which is often found in electric infrared heaters.
Enclosure Materials
Manufacturers make heater enclosures from materials that are able to endure high temperatures and effectively absorb radiant heat. This is essential, since the enclosure will be in such close proximity to extreme heat. Common materials they select include steel, stainless steel, iron, copper, brass, or aluminum.
Considerations and Customization
When designing an infrared heater, suppliers must take into consideration multiple design elements. These considerations include the material choice for the shield, the heater’s maximum internal temperature, the amount of voltage needed to turn energy into infrared waves, and the maximum wattage the heater can produce. They also consider the power source (electricity or gas). To customize your infrared heater, manufacturers can add fans or other devices that redirect heat waves and spread the heat around a particular area. However, this is not a necessary feature.
Types of Infrared Heaters
Infrared heaters are available in various designs. Based on their application, we can first classify them in three basic categories – home or indoor heaters, outdoor heaters, and industrial infrared heaters. These heaters offer a broad spectrum of benefits that have ignited the adoption of these heaters at industrial and commercial levels.
Indoor heaters, also known as home heaters, are those infrared heating systems designed to heat rooms and objects inside. Examples of indoor heating systems include small space heaters, large space heaters, electric fireplaces, portable heaters, indoor infrared grills, in-wall heaters, and panel heaters.
Outdoor heaters provide heat energy to outdoor or semi-outdoor areas, like patios or porches. (Outdoor heaters that heat patios may be called patio heaters.) They work well because they heat areas and objects directly.
Industrial infrared heaters are those infrared heaters equipped to take on the task of fueling industrial projects or warming industrial buildings.
We can also categorize infrared heaters based on their heating element, power source, shape or wavelength.
Quartz heaters use heating elements either of quartz or tungsten wire encased in a quartz glass tube. Quartz, found in nature, has exceptionally high temperature resistance and durability. Quartz heaters are popular in medicine and healthcare, animal incubation, space heating, industrial drying, food processing, chemical processing, and glass curing and processing.
Ceramic heaters are, as their name implies, infrared heaters powered with ceramic heating elements. They are available in three main types, based on heater element shape: flat heater element, trough or concave heater element and Edison screw or bulb heater element. They provided long wave infrared radiation at between 2 and 10 µm. Their most common application is animal care.
Electric infrared heaters are used in applications that require immediate heat, such as household appliances. For this reason, manufacturers usually use coiled tungsten wire as their heating element. Electric infrared heaters are efficient and inexpensive to use.
Gas-based infrared heaters create heat by converting the heat energy given off by a gas flame into electromagnetic radiation. This gas flame is usually fueled by natural gas, propane or, occasionally, petroleum. To work, the heaters utilize a group of reflectors coupled with ceramic heat exchangers, tubes, or filaments. While gas infrared heaters work quite well, they can be quite expensive, and they are not the best choice for the environment.
Tube heaters are any infrared heaters that have their heating elements encased within a radiant tube. Many different types of heaters can be tube heaters, including electric heaters and gas heaters.
Heat lamps are electrical lamps that use infrared light bulbs to emit heat energy onto people and in rooms. People often use heat lamps in physical therapy and skin treatment.
Short wave infrared heaters, alternatively known as near infrared heaters (NIR), function at a filament temperature range exceeding 1800℃, with power densities up to hundreds of kW/m2. Because their peak wavelength is far below water’s absorption spectrum, these heaters are not generally compatible with drying. Instead, they are best-suited to deep heating silica.
Medium wave infrared heaters, along with carbon infrared heaters (CIR), function with filament temperatures near 1000℃. Medium wave infrared heaters have power densities reaching 60 kW/m2, while CIR have power densities up to 150 kW/m2.
Far infrared heaters (FIR) are a bit different than the others in this category. While the others use quartz, carbon, or high watt ceramic emitters, they use low watt ceramic plates. These plates remain cold as the heater sends out infrared radiation. Most often, far infrared heaters are used to warm small rooms (as space heaters) and expensive saunas. Because they run at such low temperatures, FIR also do not really send out dust or bothersome smells. This makes them a great choice for those with allergies and sensitivities.
Radiant heating systems deliver heat directly to a home’s floor and panels in the walls and ceiling. The systems rely heavily on radiant heat transfer, which involves infrared radiation providing heat directly from a heated surface to people and objects in the room. Radiant heating is the same as a hot stovetop item that radiates warmth to the rest of the room.
Floor heating is the name for radiant heating situated on the floor. Radiant floor heating, despite its name, relies mainly on convection, or the natural movement of heat inside space as the air heated by the floor rises.
- Radiant heaters allow livable areas with invisible hardware.
- They are cost-effective and energy-efficient.
- They are compatible with smart thermostats.
- There are fewer restrictions on interior design.
- Electric radiant floor heating systems don’t need to be serviced or maintained regularly.
- Radiant heaters are suitable for any flooring.
- Installation is easy when new flooring is placed; electric-based radiant floor heating systems are simple to install.
- Regarding air quality, radiant heat is a far superior option.
- A radiant floor heating system warms a room by directly heating the floor rather than warming the air in the room, using thermal radiation and electromagnetic waves.
- Radiant heating systems warm the floor, which radiates up and is absorbed by other items in the room, thus warming the whole space.
- Heated floors, in brief, employ radiant heat technology to warm the flooring, and the heat rises and disperses throughout the space.
- Maximum operational (sheath) temperature, kilowatts, AC voltage, and maximum watt density are all important factors when selecting radiant heaters.
- The maximum operating temperature is the highest temperature that the radiant heater’s sheath can attain.
- Radiant heaters’ available wattage is usually measured in kilowatts (kW).
- The AC voltage required to run the heater must be known.
- The maximum watt density of a radiant heater is the number of watts it can deliver per square inch. Watt density is a valuable indicator of a heater’s capacity to heat a substance fast.
- The heated length must be known as it is the essential dimension of the radiant heater.
Applications of radiant heaters can be found:
- Inside big plants
- Inside garages and loading docks
- Heating tight warehouse aisles
- Heating hoppers and dry paint
- Preventing pipes and valves from freezing
- Radiant flat panel heaters are used in space heating, drying and curing, water evaporation, and food processing.
- Used in addition to sterilization, material preparation, bonding and joining, and industrial manufacture and production.
Electric Radiant Heating Systems have electric coils that create heat when electricity travels through them in an electric radiant heating system. These metal coils have a high resistance to electricity. When electricity travels through the coil, the resistance generates heat. Insulation is provided via polymer sheets wrapped around the coils.
Hydronic radiant heating systems employ a boiler to circulate warm water throughout a home or floor via a network of pipes. While they are less expensive to run than electric heating systems, they have the potential to break pipes or leak.
Air radiant heating systems utilize heat transfers through heated air. These are the least efficient of the three typical radiant heating systems because air has the least ability to carry and retain heat.
Advantages of Infrared Heaters
Ease of Use
Infrared heaters offer users a wide range of benefits. First, because infrared heaters (generally) work using electricity, they are very easy to control.
Efficiency
Second, they are much more efficient than ordinary gas heaters and UV lamps. Additionally, infrared heaters can provide quicker and more resourceful heating to your rooms and applications. They warm your room faster than any other heater can. Also, infrared heat can transfer to gases and other materials more easily than the heat waves generated from a typical convection heater.
Evenness of Heating
Infrared heaters do not need air molecules to transport the heat they generate. As a result, infrared heat can heat an object or a room evenly. In contrast, conventional heaters leave pockets of cooler air per the room’s convection currents. Due to the fact that conventional heaters require air to transport the heat they generate, they cannot uniformly heat a room as well as an infrared heater can.
Greenness
Infrared heaters are energy efficient, since their heating can be set per the application type and need. Furthermore, these heaters are more eco-friendly, or “green,” than other varieties of the industrial heater. This is because, in addition to being energy efficient, electric infrared heaters do not release pollution or harmful gases, and they do not convert oxygen into carbon dioxide.
Safety
The fact that electric infrared heaters do not burn fuels and do not emit fumes that are hazardous to the environment also means that they come with minimized health risks. Infrared heaters do not produce high carbon dioxide volumes, and thus do not remove oxygen or moisture from the surrounding air. Because of this, infrared heaters are safe to use for residential and livestock heating.
Economics
It is more economically beneficial to use infrared heaters in the place of forced air heaters, especially in applications such as space heating, curing, and drying.
Infrared Heater Proper Care
Infrared heaters are incredibly useful, but if you do not take care of them properly they can become inefficient or downright dangerous. Avoid such pitfalls by taking the following advice:
Do’s
Use a rag to clean the reflector surface anytime you see debris or dirt. Make sure you never miss anything by checking on it routinely. During your routine checkup, also inspect your reflector for sagging, distortion, and cracking. If you find any of these issues, turn off the heater and call your supplier for repair or parts replacement services. Similarly, regularly check your heater enclosure for cracks, gaps in the seals, and corrosion. Once again, if you find any of these, stop using your heater.
Don’ts
To avoid accidents and/or the untimely demise of your infrared heater, never hang clothes on the heater or underneath the heater. Also, do not stuff anything between the heater spaces or tubes. If you do that, you risk starting a fire. Likewise, do not store flammable substances near your heater, as it could start a fire.
How Infrared Heaters Work?
Infrared heaters are available in various designs. Based on their application, we can classify them in three basic categories – home or indoor heaters, outdoor heaters, and industrial infrared heaters. These heaters offer a broad spectrum of benefits that have ignited the adoption of these heaters at industrial and commercial levels. You might not be familiar with the benefits of these essential appliances but ask any industry expert they will explain how important heating applications, specifically infrared heaters, are for them.
As the name goes, infrared heaters emit infrared light that we cannot actually see, but feel. Just like you how can feel the heat produced by the Sun, you cannot see that heat coming to you or around you. To see these rays, you would need special glasses. Infrared light is, in fact, a type of radiation or radiant energy that has a longer wavelength than that of normal light with an extended red edge. This radiant energy is invisible to the human eye.
Infrared heaters make use of this invisible light and energy to warm up an area or application they have been installed in. This energy does not heat up the area or space that is not in its direct contact or exposure. When you are under tree shade or in your room the infrared light of the Sun is blocked and keeps you cool, but as you come out in the light, you feel the warmth. Industrial infrared heaters work on the same principle.
Benefits of Infrared Heaters
If we would compare the efficiency of infrared heaters with that of ordinary gas heaters, we would realize why infrared appliances have a higher adoption rate these days. Infrared heaters work on electricity, because of this, they are more controlled in comparison to gas-based heaters. Additionally, infrared heaters can provide quicker and more resourceful heating to your rooms and applications. They warm your room faster than any other heater can. Further, they are energy efficient, since their heating can be set per the application type and need. Furthermore, these heaters are more eco-friendly than other varieties of industrial heaters. Electric infrared heaters do not release pollution or harmful gases, they do not convert oxygen into carbon dioxide.
Infrared Heater Standards
In the United States, it’s very important that all infrared heaters for consumers meet the standards of the US Consumer Product Safety Commission. Note that you can get an infrared gas heater certified per the Canada-US joint standards, outlined in CAN/ANSI/AHRI 1130-2015. Infrared heaters to be used internationally need to meet the standards for that country or region, such as ISO (International Standards Organization). For the most specific advice, talk to your industry leaders.
How to Choose the Right Infrared Heater Manufacturer
No matter your application, the best way to get an infrared heater that works for you is by partnering with an infrared heater manufacturer that understands your needs, is capable of carrying out your request, can create high quality work within your budget, can deliver to you in a timely manner, and can meet all of your pre and post delivery service preferences.
The best way to figure out if a manufacturer meets these standards is by talking to them. To get started, check out the list of high quality infrared heater manufacturers we’ve listed on this page. Peruse their information and pick out three or four to whom you’d like to speak at length. After you’ve spoken with each of them, compare and contrast your conversations, and choose the right one for you.
Check out our Electric Heaters website





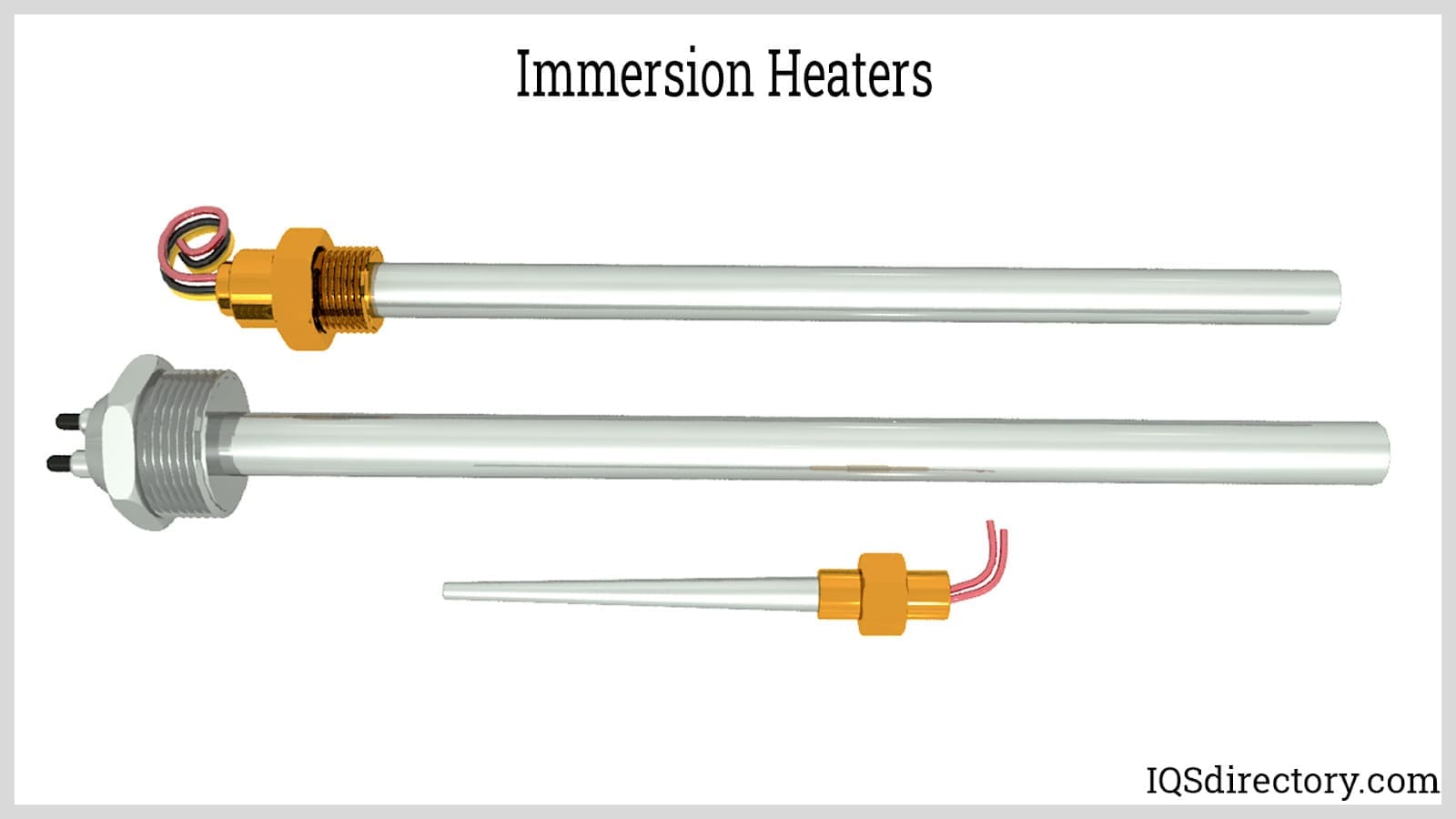
 Cartridge Heaters
Cartridge Heaters Electric Heaters
Electric Heaters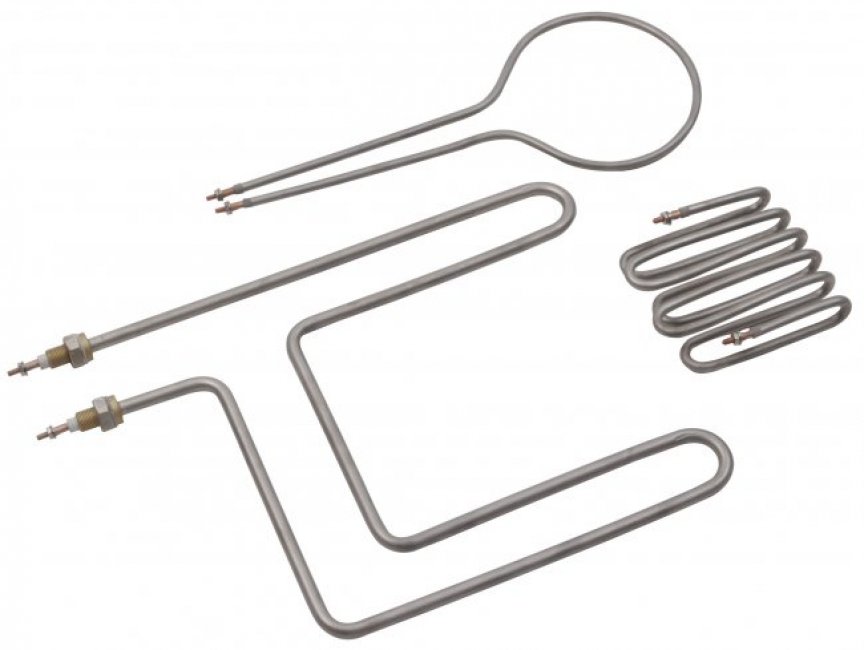 Heating Elements
Heating Elements Immersion Heaters
Immersion Heaters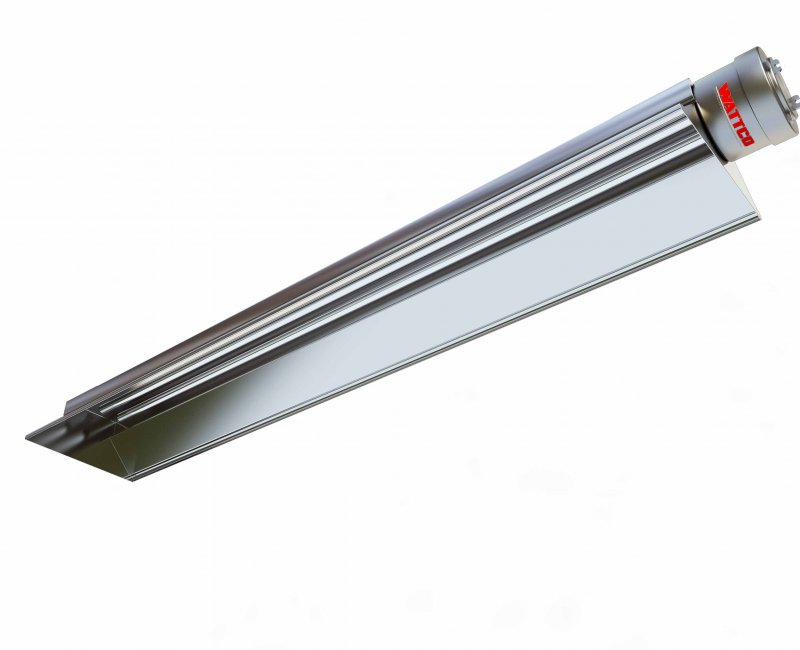 Infrared Heaters
Infrared Heaters Air Conditioners
Air Conditioners Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services